10% off £25 OR 15% off £35

Guide to SPF 2023
- Health Hub Home
- Beauty
- Skincare
- Suncare
- Guide to SPF 2023
Expertly reviewed by Dr Maha Shariff, Aesthetic Doctor & General Practitioner
Even though most of us never hesitate to apply sunscreen on holiday or on sunny days at home, digging out a bottle in the winter may not come naturally. But is it really necessary to wear SPF in any weather?
Why should you wear sun cream and which is best for your skin type?
With the advice of Aesthetic Doctor & General Practitioner Dr Maha Shariff, we’re here to help. We’ll explain what SPF is and how it works. Then, we’ll advise which SPF is right for you, based on your skin type.
That way, you’ll have a good idea of how to protect yourself from skin damage due to UV (ultraviolet radiation) throughout the year.
Skip to:
What is SPF?
SPF stands for ‘sun protection factor’. SPF is a measure of how much protection sunscreen products offer against UVB rays.
In total there are three types of UV rays, UVA, UVB and UVC. UVC, although most damaging, is filtered by the atmosphere, so we mostly hear about UVA and UVB. Whilst UVA accounts for 95% of radiation reaching the earth's surface; it penetrates deeper and is present all year round.
UVA ray protection is typically indicated by an additional tiered star system, also called a PA rating in the USA and Japan. So, if it says it has “broad spectrum” protection, it will protect again both UVA and UVB.
Out of the three UVs, UVB does not penetrate the skin as deeply as UVA, however, causes the majority of sunburn. They also play the greatest role in causing skin cancers, which include the deadly black mole form of skin cancer, malignant melanoma.3
Meanwhile, UVA rays can also contribute to skin cancer. They penetrate more deeply into our skin and play a greater role in premature skin ageing, such as wrinkle formation.


Furthermore, up to 80% of the signs of ageing we see affecting our skin such as lines, wrinkles, sun spots etc are due to exposure to UV light. 4
The longer you stay in the sun without sun protection, the greater your chances of burning. In fact, tanning and sunburn indicate damage to your skin as your melanocytes (cells that produce pigment) produce more melanin in an attempt to protect cell DNA from damage.
The sun in the UK is strongest from March to October, so it’s wise to apply a sunscreen that will provide you with protection of at least SPF 30.
This said, UVA rays are present all year round so using an SPF is a great addition to your morning skincare routine and an investment in your skin health.
Why wear SPF?
Make sure to wear an SPF of factor 30 or above throughout the year. If you tend to spend a lot of time outdoors – such as working outside – you should wear SPF 30 or higher sun cream which is also water-resistant.
It’s important to ensure the correct amount is being used and you are remembering to sweep over the upper and lower lids and lips.
The skin is more delicate in these areas, and whilst there may be lip balms with an SPF, these are often 15 or under.


Physical sun protection is also important when on holiday or hot days, so invest in hats, sunglasses, clothing, as well as avoiding times of peak sun.
Regardless of how strong your sunscreen is, if you sweat or get wet, you must put some more on again, ideally every two hours, to make sure your skin stays fully protected.5
Summary
- SPF measures how much protection sunscreen products offer against UVB rays
- Sunlight produces UVB and UVA rays
- They can both cause skin cancer
- It’s recommended to wear an SPF as part of your skincare routine, even on cloudy days
What does the number mean on SPF?
The numbers you see on your sun cream or lotion, spray or gel are ratings based on the level of protection they offer. For example, factor 2 offers the lowest form of UVB protection and SPF 50+ offers the strongest protection.
The number doesn’t relate to how long you can stay out in the sun. It applies to how much longer it will take skin that’s untanned to start to get red with sunscreen on it, compared to how long it will start to get red without it.6
And therefore, they should not be used to determine how long to stay out in the sun. SPF numbers are calculated using a certain formula. The easiest way to look at it is SPF 15 blocks 94% of UVB rays, SPF 30 blocks 96% of UVB rays and SPF 50 blocks 98% of UVB rays – when applied correctly.
While most of us pay attention to SPF, the star rating on our bottle of sun lotion is also important.
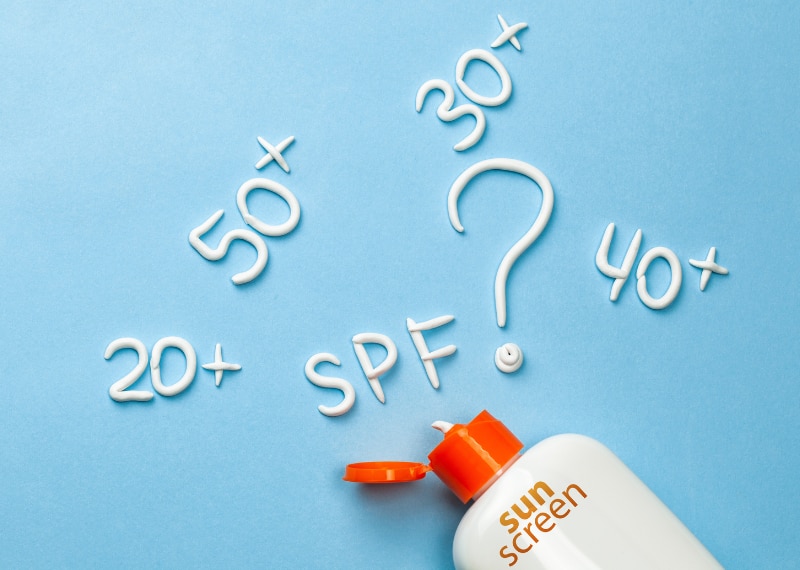
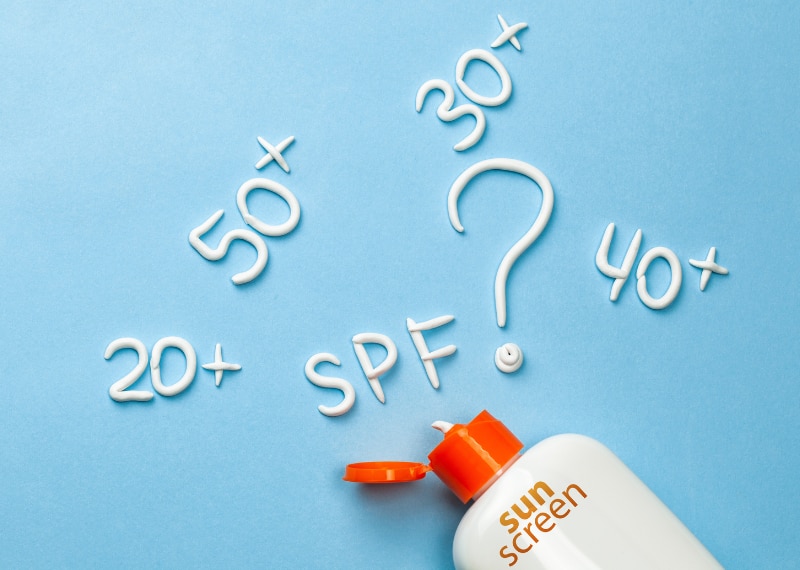
This measures the amount of ultraviolet A radiation (UVA) protection, with a rating of up to five stars being the highest shown on UK sunscreens.
UVA targets the skin more deeply than UVB and is a key factor in skin wrinkling and ageing. Choose a ‘broad spectrum’ sunscreen, as this indicates that it offers both UVA and UVB protection.
Different SPF levels
Sun creams protect you to different levels, but they’re categorised into four tiers of sun protection.
It’s important to use the correct amount of sun cream to achieve these levels of protection indicated on the product, with SPF 30 recommended as a minimum.
The tiers are:
- Low protection (SPF 4, 6, 8 and 10)
- Medium protection (SPF 15, 20 and 25)
- High protection (SPF 30, 40 and 50)
- Very high protection (SPF 50+)
What does SPF do to your skin?
SPF works by essentially creating a barrier between your skin and the sun’s UVA and UVB rays.
Some contain inorganic chemicals, such as zinc oxide or titanium dioxide, which act as a physical sunblock. They reflect UV rays, similar to how white paint reflects light.6
Physical or mineral sunscreens reflect whilst chemical or absorbing sunscreens absorb UV light and prevent it from causing damage to skin. There are also mixed sunscreens that are both chemical and physical.
Sunscreens also contain organic chemicals, such as avobenzone or oxybenzone. Instead of physically deflecting UV light, these molecules absorb UV radiation through their chemical bonds.
As the bonds absorb UV radiation, the components of the sunscreen slowly break down and release heat, slowly breaking it down to release heat, preventing it from causing damage to skin.


Summary
- Factor two offers the lowest form of UVB protection and SPF 50+ offers the strongest protection
- The number doesn’t relate to how long you can stay out in the sun for
- SPF 15 blocks 94% of UVB rays, SPF 30 blocks 96% of UVB rays and SPF 50 blocks 98% of UVB rays when applied correctly
How to choose SPF number
It’s recommended to use an SPF 30 or above all year round. However, if you have sensitive skin or are fair, consider using a factor 50 and scalp sun protection.
You’re advised to protect children with no less than an SPF 50 or to choose very high protection for especially fair children and babies.
Different types of sun cream
Widely available sun protection varieties include:
- Mineral sun creams (these are free from oxybenzone and octinoxate8)
- Cream sun cream
- Spray sun cream
- Moisturiser with SPF
- Broad-spectrum (protects from UVA and UVB rays)


Which SPF should I use?
Just one look at the different sunscreen products available, online and in-store, can be a bit mind-boggling, especially when you need to consider SPF strength and UV star rating, as well as the product type, brand and customer reviews etc.
It is important you do your research when you buy your sunscreen because it does an extremely important job and you want your skin to be as protected as possible.
Just as you would take your skin type (normal, dry, sensitive, oily or combination) into account when you’re choosing a skincare product, you need to do the same when you’re shopping around for an SPF too.
-
SPF for oily skin
Look for lighter weight, oil free products, as well as non-comedogenic options to avoid clogging pores.
Quite a few sunscreens that have a high SPF factor tend to have a thicker consistency, and this heavier consistency can leave your skin feeling clogged and sticky.
This is far from ideal, especially if your skin is already quite greasy - your pores are already prone to getting clogged and developing blemishes. 8
Look out for: Oil-free, lightweight creams, gels, fluids, lotions and mineral powders that won’t leave your skin feeling greasy or congested.
-
SPF for sensitive skin
SPFs that don’t contain certain ingredients, particularly alcohols or essential oils, that can irritate skin get on better with sensitive and blemish-prone skin.
If your skin is extremely sensitive, try a mineral powder sunscreen instead. However, as it can be rubbed off more easily, so remember to reapply.
Look out for: Lightweight or mineral powder sunscreens that contain minimal ingredients and no fragrances that can aggravate skin.
-
SPF for dry skin
Choose lightweight, hydrating SPFs that also act as a moisturising face cream. They deliver a double action boost by hydrating skin as well as protecting it from the sun.
Look out for: Hydrating and moisturising SPFs that are packed full of moisture and don’t overwhelm skin.
-
SPF for combination skin
Stick to a lightweight SPF that will provide protection without flooding your skin with too much heavy product and block your pores, while also providing moisture where it’s needed too.
Look out for: SPF gel formulations that aren’t too thick or greasy, but will still provide adequate moisture.
-
SPF for your eyes and lips
Just as there are moisturisers with SPF and face cream with SPF, there are specific sunscreen products for protecting the skin around your eyes, your lips and your hands from the sun too.
However, these are sometimes only SPF 15 and so using regular sun cream and gently applying to the face will give you the protection you need.
Look out for: Lip balm with SPF, eye cream with SPF and hand cream with SPF that have been specially formulated to protect while also taking care of your lips, delicate eye area and hands.
-
SPF for dark skin
If you have a dark complexion you’ll also need to use SPF, as your skin can still burn and get damaged by the sun.
Regardless of skin colour an SPF 30 or above is recommended. Whilst melanoma rates are lower in darker skins, they are also prone to pigmentation and melasma, so SPF is a defense against this.
Look out for: Factor 30 or above, well-absorbing, perhaps a tinted product to suit your skin tone.
-
SPF for pale skin
If you have pale skin, you’ll likely need high to very high protection SPF as your skin will burn quicker than those with darker skin tones.
Look out for: Factor 50, mineral or chemical sunscreen formulation.
Which SPF is best?
At least a four-star UVA protection and SPF 30 is recommended for most people as a shield against the sun’s rays. However, this can differ depending on your skin type.
For a boost of added moisture, those with dry skin should opt for cream or gel-based products. If you have oily or spot-prone skin, oil-free sunscreens will protect you from the sun without clogging your pores.
Mineral, oil-free, fragrance-free and hypoallergenic products are ideal for sensitive skin as they contain fewer chemicals.
Summary
- Choose an SPF based on your skin type
- Lightweight SPFs are better for oily or combination skin. Moisturising SPFs are better for dry skin
- A minimum 4-star UVA protection, ideally 5 star, and SPF 30 and above is recommended for most people.


How to use SPF
Getting the right SPF for you is one thing, but using it properly is equally as important.
How much to apply
If you’re going to have a lot of your skin exposed to the sun, then you’ll need at least a thumb-sized amount of SPF for your whole body – a teaspoon sized dollop for each arm, leg, your front and your back.
A guide to how much sun cream to wear on your body:
- Face and neck – 1/2 a teaspoon
- Arms – 1 teaspoon
- Legs – 2 teaspoons
- Front and back of the torso – 2 teaspoons
When to apply
Be sure to apply your SPF last, so after you’ve used any serums or moisturiser. If it’s a mineral sunscreen you should be good to go out in the sun straight away, but if it’s a chemical one you’ll have to wait 15-30 minutes for it to sink in.
And it’s super important to reapply every two hours or after you’ve been in water or exercised.
Which ingredients you can and can’t you mix it with:
Try not to mix your own SPF/moisturiser or makeup hybrid as this will affect the efficacy of the product.
Always wear SPF if you use retinol, vitamin C skincare products, benzoyl peroxide, AHA/BHA acids. It is important to only use retinol at night too, as it is an active ingredients which may increase skin sensitivity.
Do you need to wear sunscreen in the winter?
Though it may be cold outside and summer is long gone, you’re still at risk of burning or UV damage, even on cloudy days. In winter, reflected light from snow, sand and water can also intensify your exposure to UV rays.
Even if you are spending a short period of time outside in the winter sun, an SPF or adequately high SPF-containing moisturiser will help protect you against these periods of UV exposure.


Does wearing SPF all year lead to vitamin D deficiency?
Vitamin D is created by our bodies from direct sunlight on our skin when we’re outside.
From October to March, sunlight doesn’t contain enough UVB for our bodies to synthesise vitamin D.
However, sun safety is still important so make sure to protect your skin whenever it’s exposed to the sun and SPF application does not prevent vitamin D production.9
Eating oily fish, eggs or using a supplement are alternative sources of vitamin D.
Summary
- You can still get sunburnt, even on cloudy days
- SPFs shouldn’t just be worn during the summer
- Sun safety is still important, as well as vitamin D absorption
Which skincare ingredients boost SPF effectiveness?
There are a few skincare ingredients that may be able to bolster your SPF protection, these include vitamin C, vitamin E, and ferulic acid which can be found in serums, however, they are not alternatives to SPF, which is our skin's best protection against UV damage.10
A final few words about SPF…
Just as you may not be able to live without your favourite stay-put lippie or double length mascara, the same principle applies to SPF too – it’s a skincare staple for your face and body that should never be overlooked.
The great thing is, there are so many different sunscreens available.
Not only are they suitable for all types of skin, but they’re available in a form that works best for your skin, e.g. gel, mineral or serum, foundation or moisturiser, as long as they meet the standard of SPF 30.


If it isn’t already in there, add SPF into your daily skincare regime, and if it is, great news, keep applying it every day.
- https://uihc.org/health-topics/what-difference-between-uva-and-uvb-rays
- Amaro-Ortiz A, Yan B, D'Orazio JA. Ultraviolet radiation, aging and the skin: prevention of damage by topical cAMP manipulation. Molecules. 2014 May 15;19(5):6202-19. doi: 10.3390/molecules19056202. PMID: 24838074; PMCID: PMC4344124 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4344124/
- https://www.skincancer.org/skin-cancer-prevention/sun-protection/sunsc5reen/
- https://www.science.org.au/curious/people-medicine/what-does-spf-rating-really-mean
- https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/news/sunscreen-corals.html
- Suh S, Pham C, Smith J, Mesinkovska NA. The banned sunscreen ingredients and their impact on human health: a systematic review. Int J Dermatol. 2020 Sep;59(9):1033-1042. doi: 10.1111/ijd.14824. Epub 2020 Feb 28. PMID: 32108942; PMCID: PMC7648445. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7648445
- https://www.nhs.uk/live-well/seasonal-health/sunscreen-and-sun-safety/
- https://www.bad.org.uk/sunscreen-application-does-not-prevent-vitamin-d-production-in-the-majority-of-people/
- https://projectsunscreen.com/blogs/news/how-to-choose-the-right-sunscreen-for-different-skin-tones

Aesthetic Doctor & General Practitioner
MRCGP Member of the Royal College of General Practitioners, London, 2015
Dr Maha Shariff is an Aesthetic Doctor and General Practitioner in the NHS.
As an Aesthetic Doctor, the areas Maha specialises in include skin treatments and non-surgical aesthetic treatments. Maha is passionate about skin health and helping her patients to look and feel their best, understand how to look after and love their skin. She believes that you deserve healthy, radiant skin at every age.
She works in a GP Surgery in North London, having completed her GP training from the prestigious St Mary’s GP Training Scheme in 2015. She loves the continuity of care and really getting to know her patients, having been inspired by her own GP. She feels blessed for the opportunity to make a positive difference in people’s lives through both her aesthetics and NHS work.
In her spare time, Maha enjoys time with her family, making delicious home cooked food, gardening and travelling.
Education
- MBBS Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry, London, 2007
- BSc Medical Management, Imperial College, London, 2006
- DRCOG Diploma of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, London, 2011
- MRCGP Member of the Royal College of General Practitioners, London, 2015
Affiliations/Memberships/Governing bodies
- GMC (General Medical Council)
- RCGP (Royal College of General Practitioners)
- BMA (British Medical Association)
- Hamilton Fraser Cosmetic Insurance


