10% off £35
Collagen & Silica



















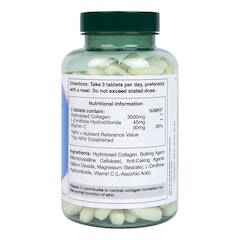




















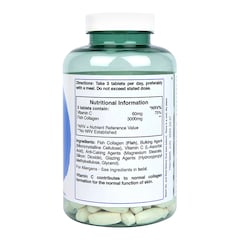











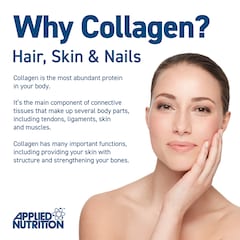

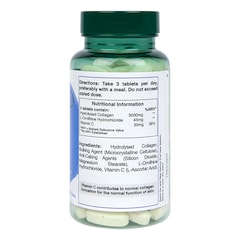























































It’s easiest to think of collagen as the building blocks of the body. Categorised as a structural protein, it connects tendons, ligaments and muscles and gives your skin its elasticity and structure – it’s also the basis of strong and healthy bones.
Specific amino acids like glycine, proline hydroxyproline and arginine all feature in collagen. You’ll find many of these in supplement form and in a variety of high protein foods, including bone broth.
In addition, collagen is also the most common protein in the body, where it’s naturally produced. So why would you ever need collagen supplements?
For starters, your body begins to slow its collagen production after you reach 25. Another reason to explore collagen supplements is that smoking, ultraviolet light from the sun and consuming excessive sugar can decrease your collagen levels.
The bodies of all animals, including humans, contain large amounts of the protein collagen. Collagen is what adds structure and strength to skin, as well as to organs, bones, tendons and ligaments.
Marine collagen is a type of collagen protein sourced from fish and other sea life, such as jellyfish. It’s a growing market, with public demand increasing following a series of successful studies into its effectiveness. Find out more about marine collagen.
Collagen’s perceived benefits have been written about extensively.
Here are just a few of the most common benefits written under review:
- Bone health – collagen contributes to normal function of bones
- Skin and nail health – collagen contributes to maintenance of normal skin and nails
- Joint health – collagen helps maintenance of cartilage in the body which is integral to good joints
Find out more about collagen and its benefits as well as top tips, expert advice and FAQs over on our Collagen Hub.
If collagen is in all of us, silica is found everywhere else. A natural compound, it makes up over a quarter of the Earth’s crust and is found in rocks, sand and even some foods. Like collagen, silica has many different perceived benefits. These include the following:
- Bone formation and maintenance – silica may help to improve your bone health, with a deficiency in silica believed to be partly linked to cartilage deterioration
- Collagen production – some studies show silica can help your body’s production of collagen, which you’ve already read is linked to a number of skin and bone benefits
The list of foods that contain silica includes but isn’t limited to:
- Wholegrains
- Green beans
- Rice
- Cucumbers
- Tomatoes
Similar to collagen, silica can be found in supplement form, with a range of silica capsules and tablets available on our website from leading supplement brands.
Silica supplements are an excellent choice if your diet contains few of the above foods, or simply if you’re looking for supplements to add to your cabinet.
Hydrolyzed collagen, marine collagen, bovine collagen, eggshell membrane and gelatin are the most used types of collagen in supplements, which all come from animal sources such as hides, bones, or fish scales.
Vegan collagen support supplements have been developed to include ingredients like Vitamin C which support normal collagen formation to support the health of bones, cartilage, skin, blood vessels, gums and teeth.
Take a look at the Starpowa Vegan Collagen support gummy here.
Collagen powders and creamers can come in a variety of different flavours including vanilla, caramel, cherry, chocolate and more.
You can also get powders and creamers that are unflavoured, for those not wanting flavoured options.
Yes, there are a variety of unflavoured collagen supplements for those who are wanting to add collagen to food and drink, but don’t want to affect the taste.
There is the misconception that collagen isn’t absorbed by the body. However, research has shown that key peptides within collagen are taken from the GI tract and delivered to tissue such as the skin.
To best preserve your collagen supplements, it is recommended to store products in a cool, dark area that is away from any moisture or sunlight.
The body’s natural collagen production starts to slow down when we are in our 20s. This decline in production causes the ageing of our skin and joints.
There’s a myth that you don’t need to consider using these products until you are in your 40s, but there is no harm in starting earlier.
The idea that your collagen supplement will either be destroyed or disrupted by digestive acid in the stomach is a myth. Collagens supplements are usually broken down by your stomach acid, with or without food, into amino acids that are then used to build more collagen.


